State of Palestine
Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS)
Press Release
17 October 2016
Ramallah
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS) and Food Security Sector (FSS) are pleased to announce the launch of the final results of the Socio-Economic and Food Security Sector Survey (SEFSec) 2014 for Palestine.
According to the report, more than one fourth of Palestinian households, or 1.6 million households, are significantly or moderately food insecure, with a considerably higher rate – 47 percent – observed in the Gaza Strip. This food insecurity is characterized by a lack of economic access to food, which is strongly linked with the high prevalence of unemployment, and compounded by restrictions on access to natural resources such as land and water as well as the movement of people and goods and can only be fully addressed if its root causes – including the blockade of the Gaza Strip and restrictions on the West Bank – are resolved.
The 2014 report builds on the work of SEFSec reports produced since 2009 and introduces a new methodology that incorporates resilience as well as comparatively analyses food insecurity in 2013 and 2014. It is the product of a collaborative effort between PCBS and the FSS, co-led by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Food Programme (WFP) in close collaboration with UNRWA and includes an intensive and participative process that started in 2015 that involved United Nations agencies, non-governmental organizations and Palestinian line ministries, with PCBS conducting the survey.
This launch coincides with World Food Day 2016, which highlights the complexity of addressing global food insecurity by emphasising the linkages between agriculture and climate change as well as the need to build global food security on a foundation of sustainable agricultural practices. Robust data are essential to meeting this challenge. Indeed, for Dr. Ciro Fiorillo Head of the FAO Coordination Office for West Bank and Gaza Strip, “the data and analysis provided in this report are essential to better understand the determinants of food security specific to the local context and shaping interventions able to support the Palestinian people in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).”
Promoting the use of innovative programming to bring Palestine closer to achieving these goals depends on matching humanitarian and development actors’ interventions with the needs of Palestinians. Here again, the data of SEFSec are essential. As noted by Daniela Owen, WFP Representative and Country Director in Palestine, “the findings of the report not only underline the criticality of providing food assistance to people in need, but are instrumental to help tailor targeted and multi-sectoral interventions, together with the Palestinian authority and other partners, to ensure sustainable impact.”
The indicators of SEFSec 2014 assess many socio-economic and environmental aspects of food insecurity and establish a comprehensive database on these indicators as well as evaluate the impact of Israeli Aggression on the Gaza Strip in 2014. The survey design and implementation represent a step forward in statistics since it uses panel sample based on the same sampling units of the previous year of 2013 to track the changes on these units including the split households of the original sample that provide a complete database which allows for comparisons with the last two years. The indicators of the survey also cover all socio-economic and environmental factors that affected the individuals and households during and after the Israeli Aggression on Gaza Strip in the second half of 2014.
The survey sample comprised 9025 households, while the data collection took place in the first half of 2015
In addition to this launched report, a statistical report is available. The main findings of the survey, supplemented by the methodology and data quality that includes the survey questionnaire, sampling frame, field operations and data processing, in addition to the concepts and definitions that used in the survey.
Survey Findings showed that the percentage of households who received assistance in 2014 compared to 2013 has increased by 7.2%. The rise according to region showed that it was small in the West Bank compared to the Gaza Strip. The increase of assistance reception increased by 1.2% in the West Bank compared to 2013, while it increased by 18.4% for households in the Gaza Strip in the same period.
Percentage of Households Who Received Assistance in 2013, 2014
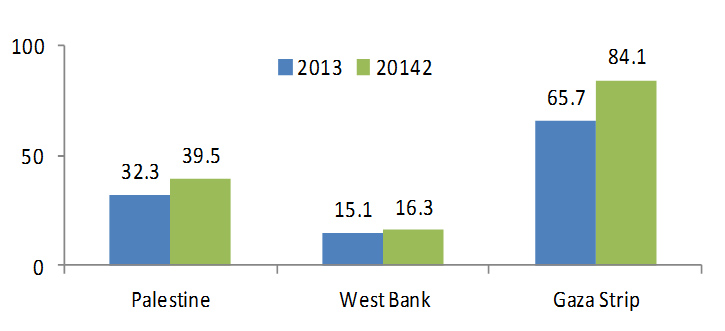 <>
<>
Survey findings for 2014 showed that 39.6% of households who received assistance in Palestine received food assistance. Cash assistance represented 17.5% and housing assistance constituted 13.4%. The percentage of assistance received by Palestinian households in the form of food ratio was 10.5% while health insurance assistance represented 10.2%.
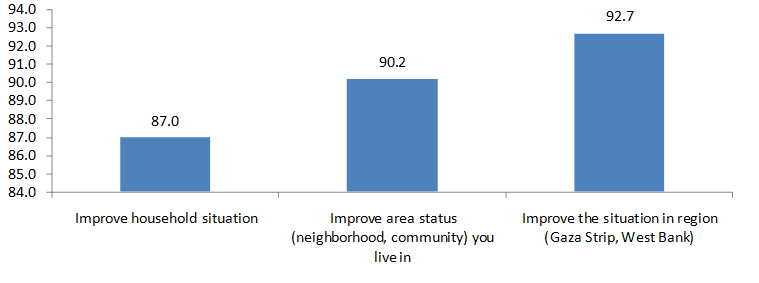
As regards households’ opinion of the impact of assistance, data showed that 87.0% of households in Palestine believe that assistance helped improve households living conditions while 90.2% believe assistance helped improve the situation in their area (neighborhood, street, community). On the other hand, the percentage of households who believe that assistance helped improve living in the region (West Bank and Gaza Strip) reached 92.7%.
Percentage of Palestinian Households (regardless if they received assistance or not) Who Believe that
45.4% of households in Palestine reported they purchased their food needs on credit because they cannot pay cost (35.4% in the West Bank and 64.6% in the Gaza Strip). As for the distribution of households that buy their food needs on credit because they cannot afford cost per governorate, Jericho and Jordan Valley scored highest with 61.7%, and the lowest Ramallah and Albiereh with 21.2%; in the Gaza Strip, the highest rate was in Dier AlBalah scored highest with 74.5% and the lowest in Gaza Governorate (59.8%).
Findings showed that a 6.1% increase in the number of households that buy their needs on credit because they are unable to pay cost in 2014 compared to 2013. In the West Bank, the rate increased by 2.3% compared to 2013. This rise was more noticeable in the Gaza Strip, marking 13.4% for the same period.
The Palestinian private sector comes on top of the list of sources of income in Palestine. 30.1% of Palestinian households reported that their main income came from the private sector (34.4% in the West Bank and 22.0% in the Gaza Strip). The public (government) sector ranks second source of income with 20.9% of households reporting it was their main source of income (13.0% in the West Bank and 35.9% in the Gaza Strip). The third main source of income was labor in Israeli sectors, (12.9% of households).
Findings showed that the living conditions of households in the Gaza Strip have noticeably deteriorated in the second quarter of 2014 as 36.0% of households reported they were in worse living conditions, compared to the second half of 2014. On the other hand, 21.4% of households in the West Bank reported the same. Moreover, 29.1% of households in the Gaza Strip reported that their living conditions are much worse compared to 3.7% in the West Bank.
63.5% of Palestinian households can survive regardless of duration (80.0% in the West Bank, compared to 32.9% in the Gaza Strip). Findings showed that 29.6% of Palestinian households barely manage and endure dire financial situation. 14.8% of these households are in the West Bank, compared to 57.3% in the Gaza Strip.
It is evident that restrictions on mobility constituted a major problem for Palestinian households in 2014 compared to 2013 with a 19.2% rise in the percentage of households who reported that such restrictions represented a major problem. The more noticeable increase was in the Gaza Strip, showing a rise of 51.8% in 2014 compared to 2013, compared to 2.6% increase in the West Bank for the same period.
Findings of 2014 survey showed that 83.7% of Palestinian households have not or any of their members thought of immigrating since 2009 (90.6% in the West Bank and 70.1% in the Gaza Strip).
As for households or any of their members thinking of immigrating, findings showed that 9.3% of Palestinian households have at least one member who thinks of immigrating; 3.5% have several members who think of immigrating and 3.5% of households think of immigrating entirely.
President of PCBS; Ms. Ola Awad hopes that the final report of this survey as well as the statistical report fills a gap in statistical data that can be used as reference for the Palestinian official statistics as well as all stakeholders to help in planning and decision making towards the sustainable development as the core of 2030 agenda.
 عربي
عربي