Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS)
On the Occasion of the World Health Day, 07/04/2023
Health services in Palestine
Four main sectors supervise the provision of health services in Palestine; the government health sector (Ministry of Health and Military Medical Services), UNRWA, NGOs and the private sector. These sectors played a complementary role in improving health services and the health situation in Palestine over the past decade. The number of primary health care centres increased from 706 centres in 2010 to reach 765 centres in 2021. The Ministry of Health bears the greatest burden, as 64% of the primary centres are affiliated to the Ministry of Health, followed by NGOs by 25%, UNRWA by 9% and Military Medical Services by 2%. The number of hospitals also increased from 76 in 2010, distributed to 51 hospitals in the West Bank and 25 in Gaza Strip, reaching 89 hospitals in 2021 (54 hospitals in the West Bank and 35 in Gaza Strip). The total number of hospital beds in Palestine in 2021 was 7,296 beds (4,270 in the West Bank and 3,026 in Gaza Strip).
Health forces play a major role in improving health status and increasing access to required health services. Since 2010, the number of physicians registered in the Medical Association increased from 6,764 physicians to 14,054 in 2021(8,001 physicians in the West Bank and 6,053 physicians in Gaza Strip). As for the number of nurses, it increased from 10,520 nurses in 2010 to 22,478 nurses in 2021 (11,494 nurses in the West Bank and 10,984 nurses in Gaza Strip).
Percentage of Total Current Health Expenditures to Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The percentage of current health expenditure to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Palestine at current prices was 10.4% in 2021 and 10.3% in 2020. Total health expenditure per capita was USD 383.9 in 2021 and USD 332.3 in 2020.
High prevalence of chronic diseases
The percentage of individuals aged 18 years and above with at least one chronic disease has increased slightly over the past decade, reaching 18% in 2010, while it reached about 20% in 2021. The prevalence of chronic diseases increases with age, where data showed that more than two-thirds of the elderly in Palestine in 2021suffer from at least one chronic disease. This percentage varied greatly between males and females, reaching 66% and 76%, respectively.
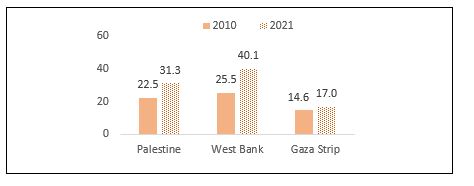
A significant increase in smoking rates and a significant gap between the West Bank and Gaza Strip
Since 2010, percentage of smoking among individuals aged 18 years and above has increased in Palestine to reach about 31% in 2021, while it was about 23% in 2010. At the region’s level, data indicated a large gap between the West Bank and Gaza Strip. There’s a clear increase in the prevalence of smoking among individuals aged 18 and above in the West Bank, as it increased from about 26% in 2010 to about 40% in 2021. In Gaza Strip, it increased from about 15% in 2010 to 17% in 2021. Manufactured cigarettes constitute the most common type of smoked tobacco among male smokers, with a percentage of 68%, while water-pipe smoking constituted the highest percentage among female smokers out of all types of smoked tobacco, with a percentage of 67% in Palestine.
Smoking Percentage among individuals (18 years and above) by region in
2010, 2021
More than half of adults suffer from depression
The World Health Organization defines mental health as “a state of psychological well-being that enables a person to cope with the stresses of life, fulfil their potential, learn and work well, and contribute to their community. It is an integral part of health and well-being that underpins our individual and collective abilities to make decisions, build relationships and shape the world we live in. Mental health is a basic human right.” Data of the Psychological Conditions Survey in 2022 showed that more than half of the individuals aged 18 years and above in Palestine suffer from depression, with a wide variation between the West Bank and Gaza Strip, where the percentage reached 50% and 71%, respectively. Nonetheless, data showed that post-traumatic stress disorder among individuals aged 18 years and above is more common in Gaza Strip than in the West Bank.
A decline in infant and child mortality rates
The infant and child mortality rate is a measure of the social status and the extent of improvement and development in the health situation in any country. Palestine has achieved remarkable progress in reducing mortality rates of infants and children under five years during the past decade. As infant mortality decreased from 20 deaths per 1,000 live births during the period 1995-2010 to 12 deaths per 1,000 live births during the period 2015-2019. As for the under-five mortality rate, it decreased from 23 deaths per 1,000 live births to reach 14 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2020.
High prevalence rates of exclusive breastfeeding
The percentage of children aged (0-5 months) who were exclusively breastfed has increased significantly since 2010, as the percentage reached about 27% in and it increased in the year 2020 to reach about 43% of all children in the same age group. On the other hand, the percentage of children who were breastfed within the first hour after birth decreased from about 62% in 2010 to 41% in 2020 in Palestine. Breastfeeding within an hour after birth is an important factor in increasing the probability of the child’s survival, according to the World Health Organization.
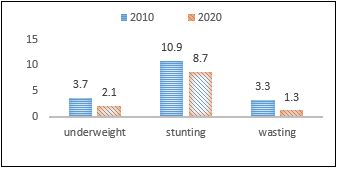
A decrease in malnutrition indicators among children
Indicators of malnutrition (underweight, stunting, and wasting) are among the important indicators that indicate the nutritional, social, and health status of children. Data showed a remarkable improvement and progress in the nutritional status of children. Data from the Palestinian Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) in 2019-2020 indicated that about 9% of children under the age of five suffer from stunting, 2% suffer from underweight, and 1% suffer from wasting, while these percentages were, for the same age group, about 11%, 4% and 3%, respectively in 2010.
Prevalence of malnutrition among children under five years of age in Palestine 2010, 2020
An increase in contraceptive prevalence
The percentage of using contraceptive methods have increased since 2010 in Palestine and significantly in Gaza Strip. The percentage of married women aged 15-49 years who or their husbands use any contraceptive methods reached about 57% in 2020; about 56% in the West Bank compared to 59% in Gaza Strip. In 2010, the percentage was approximately 52% in Palestine; 55% in the West Bank compared to 48% in Gaza Strip. Despite the increase in the use of contraceptive methods, results showed that about one woman out of every eight women has an unmet need of family planning methods in 2020. This percentage is higher in the West Bank compared to Gaza Strip, where the rates reached 14% compared to 12%, respectively.
A rise in the Caesarean Deliveries
The percentage of caesarean deliveries in Palestine reached 26% of all births in 2020; 28% in the West Bank compared to 22% in Gaza Strip. Results showed that the percentage of caesarean deliveries that were decided before the beginning of labor pains was about 18%, compared to 8% of them that were decided after the beginning of labor pains. While the percentage of caesarean deliveries was 17% in 2010; 19% in the West Bank compared to 14% in Gaza Strip.
The majority of women received healthcare during pregnancy
About 99% of women in Palestine received healthcare from skilled health personal during pregnancy, 98% in the West Bank compared to 99% in Gaza Strip in 2020. The percentage of women who received antenatal care at least 4 times was about 95%, while the percentage of those who received antenatal care at least 8 times was about 73%.
 عربي
عربي